Authentication
The initiator is the first peer who requests a connection, usually the APP reacting to a login request made by the User. The APP needs to authenticate the account that the User wants to log in with. The User has just to provide a Hive account name. No password or private key is required.
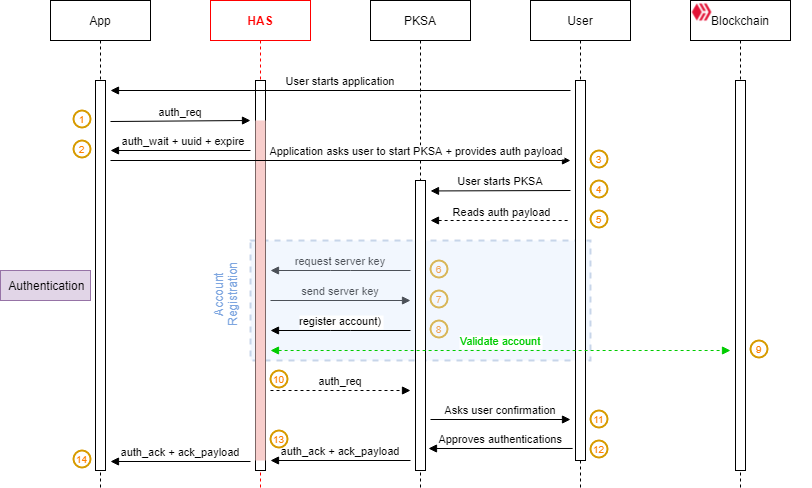
The APP sends an
auth_reqcommand to the HAS.The HAS provides the APP with a request identifier (
uuid) and a request expiration time (auth_req_expire)The APP builds an authentication payload (
auth_payload) which contains the receiveduuid, the accountname, a session encryption key (auth_key) and the URL of the HAShostit is connected to.The
auth_payloadwill be shared with the PKSA offline using a QR code or deep linking. The APP asks the User to start its PKSA and scan the QR Code or it triggers the PKSA using deep linking when on mobile.The User starts the PKSA.
Note: the PKSA can be started before or after the user starts the authentication process. It doesn't matter.
The User scans the QR code using the PKSA.
Note: This step is optional when the APP is a mobile application. The PKSA can retrieve the
auth_payloadfrom the deep link that triggered it.The PKSA asks the HAS for its public encryption key to securely register the account (
name) found in theauth_req_payload.The HAS provides its public key to the PKSA (
key_server)The PKSA asks the HAS to register the account in order to receive account-related pending requests.
The HAS validates against the blockchain that the account exists and that the PKSA stores a valid private key from the account
Note: The key ownership validation can be performed with any key. We recommend performing this process using the one that has the least permissions among those available.
Upon successful account validation, the HAS will forward the pending
auth_reqto the PKSA.Note: The PKSA must match the
auth_payload.uuidwith theauth_req.uuidit receives to ensure it is processing the correct request.The PKSA asks the User to approve or reject the authentication request.
The User approves or rejects the authentication request.
Depending on the user reaction:
if the User approves the authentication request, the PKSA:
creates an
auth_expire and stores itencrypts the
uuidwith the key (key_app) found in theauth_payloadcreates an
auth_ack_payloadwith the above data (auth_expireand encrypteduuid) and sends it with an authentication request approval message (auth_ack) to the HAS.
If the user rejects the authentication request, the PKSA sends an authentication refusal (
auth_nack) to the HAS.Note: This operation is not depicted in the above diagram for clarity.
The HAS forwards the authentication approval and its payload (
auth_ack) or the authentication refusal (auth_nack) to the APP.
The encryption performed at step 13.1 ensures that a malicious actor operating a HAS cannot bypass the PKSA to approve an authentication request by itself.
Remember that the HAS doesn't have access to key_app. Therefore, by matching the decrypted auth_ack_payload.uuid using its encryption key (key_app) with the pending request uuid it received from the HAS with the sign_wait event, the APP has 100% certainty that the encryption process was made by the PKSA.
Note: The default maximum delay to approve an authentication request is 60 seconds. The HAS will discard any pending request with a longer timeout.
Last updated